- Cisco Vpn Client Windows 10
- Cisco Anyconnect Vpn Win 10
- Anyconnect Vpn Cisco Download Windows 10
- Anyconnect Vpn Not Working Windows 10
Note
Intune may support more settings than the settings listed in this article. Not all settings are documented, and won’t be documented. To see the settings you can configure, create a device configuration profile, and select Settings Catalog. For more information, see Settings catalog.
- With AnyConnect's Network Visibility Module (NVM), you can defend more effectively and improve network operations. Defend against threats, no matter where they are. For example, with Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), you can prevent noncompliant devices from accessing the network.
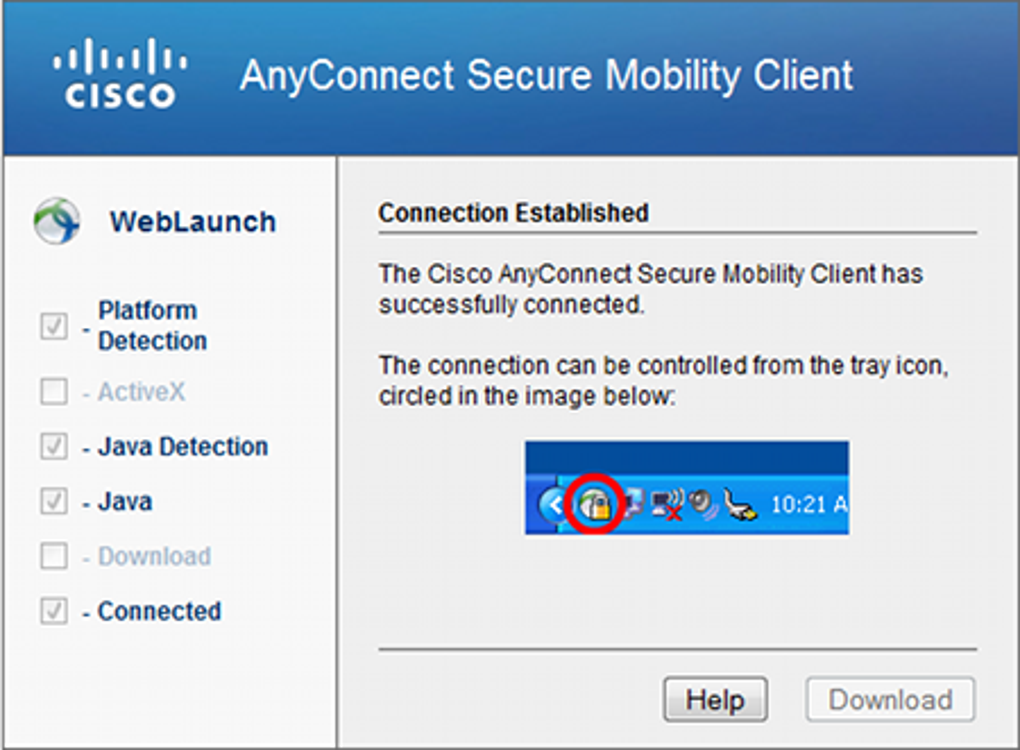
- If your Windows 10 computer has been in sleep mode or in hibernation mode before, reboot your computer. If any Windows update pending, update it. Type in search box Settings, select settingsupdate & SecurityWindows update. If your company has set password policy, need to reset the password. Cisco AnyConnect VPN client Fixes.
Overview Stanford's VPN allows you to connect to Stanford's network as if you were on campus, making access to restricted services possible. To connect to the VPN from your Windows computer you need to install the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client. Two types of VPN are available: Default Stanford (split-tunnel). When using Stanford's VPN from home, we generally recommend using the. Windows 8: On the Start screen, click Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client. Windows 10: Start All Apps Cisco Cisco AnyConnect. Alternatively, you can click Start and begin typing Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client and the application will show up. Click on the icon to start the application so you can disconnect from the VPN.
You can add and configure VPN connections for devices using Microsoft Intune. This article describes some of the settings and features you can configure when creating virtual private networks (VPNs). These VPN settings are used in device configuration profiles, and then pushed or deployed to devices.
As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to allow or disable features, including using a specific VPN vendor, enabling always on, using DNS, adding a proxy, and more.

These settings apply to devices running:
- Windows 10
- Windows Holographic for Business
Before you begin
Deploy your VPN app, and create a Windows 10 VPN device configuration profile. The available settings depend on the VPN client you choose. Some settings are only available for specific VPN clients.
These settings use the VPNv2 CSP.
Base VPN
Connection name: Enter a name for this connection. End users see this name when they browse their device for the list of available VPN connections.
Servers: Add one or more VPN servers that devices connect to. When you add a server, you enter the following information:
- Description: Enter a descriptive name for the server, such as Contoso VPN server.
- IP address or FQDN: Enter the IP address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the VPN server that devices connect to, such as 192.168.1.1 or vpn.contoso.com.
- Default server: Enables this server as the default server that devices use to establish the connection. Set only one server as the default.
- Import: Browse to a comma-separated file that includes a list of servers in the format: description, IP address or FQDN, Default server. Choose OK to import these servers into the Servers list.
- Export: Exports the list of servers to a comma-separated-values (csv) file.
Register IP addresses with internal DNS: Select Enable to configure the Windows 10 VPN profile to dynamically register the IP addresses assigned to the VPN interface with the internal DNS. Select Disable to not dynamically register the IP addresses.
Connection type: Select the VPN connection type from the following list of vendors:
- Cisco AnyConnect
- Pulse Secure
- F5 Access
- SonicWall Mobile Connect
- Check Point Capsule VPN
- Citrix
- Palo Alto Networks GlobalProtect
- Automatic
- IKEv2
- L2TP
- PPTP
When you choose a VPN connection type, you may also be asked for the following settings:
Always On: Enable automatically connects to the VPN connection when the following events happen:
- Users sign into their devices
- The network on the device changes
- The screen on the device turns back on after being turned off
To use device tunnel connections, such as IKEv2, Enable this setting.
Authentication method: Select how you want users to authenticate to the VPN server. Your options:
Username and password: Require users to enter their domain username and password to authenticate, such as
user@contoso.com, orcontosouser.Certificates: Select an existing user client certificate profile to authenticate the user. This option provides enhanced features, such as zero-touch experience, on-demand VPN, and per-app VPN.
To create certificate profiles in Intune, see Use certificates for authentication.
Derived credential: Use a certificate that's derived from a user's smart card. If no derived credential issuer is configured, Intune prompts you to add one. For more information, see Use derived credentials in Intune.
Machine certificates (IKEv2 only): Select an existing device client certificate profile to authenticate the device.
If you use device tunnel connections, you must select this option.
To create certificate profiles in Intune, see Use certificates for authentication.
EAP (IKEv2 only): Select an existing Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) client certificate profile to authenticate. Enter the authentication parameters in the EAP XML setting.
Remember credentials at each logon: Choose to cache the authentication credentials.
Custom XML: Enter any custom XML commands that configure the VPN connection.
EAP XML: Enter any EAP XML commands that configure the VPN connection. For more information, see EAP configuration.
Device tunnel (IKEv2 only): Enable connects the device to the VPN automatically without any user interaction or sign in. This setting applies to PCs joined to Azure Active Directory (AD).
To use this feature, the following are required:
- Connection type setting is set to IKEv2.
- Always On setting is set to Enable.
- Authentication method setting is set to Machine certificates.
Only assign one profile per device with Device Tunnel enabled.
IKE Security Association Parameters (IKEv2 only): These cryptography settings are used during IKE security association negotiations (also known as
main modeorphase 1) for IKEv2 connections. These settings must match the VPN server settings. If the settings don't match, the VPN profile won't connect.Encryption algorithm: Select the encryption algorithm used on the VPN server. For example, if your VPN server uses AES 128 bit, then select AES-128 from the list.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Integrity check algorithm: Select the integrity algorithm used on the VPN server. For example, if your VPN server uses SHA1-96, then select SHA1-96 from the list.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Diffie-Hellman group: Select the Diffie-Hellman computation group used on the VPN server. For example, if your VPN server uses Group2 (1024 bits), then select 2 from the list.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Child Security Association Parameters (IKEv2 only): These cryptography settings are used during child security association negotiations (also known as
quick modeorphase 2) for IKEv2 connections. These settings must match the VPN server settings. If the settings don't match, the VPN profile won't connect.Cipher transform algorithm: Select the algorithm used on the VPN server. For example, if your VPN server uses AES-CBC 128 bit, then select CBC-AES-128 from the list.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Authentication transform algorithm: Select the algorithm used on the VPN server. For example, if your VPN server uses AES-GCM 128 bit, then select GCM-AES-128 from the list.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Perfect forward secrecy (PFS) group: Select the Diffie-Hellman computation group used for perfect forward secrecy (PFS) on the VPN server. For example, if your VPN server uses Group2 (1024 bits), then select 2 from the list.
When set to Not configured, Intune doesn't change or update this setting.
Cisco Vpn Client Windows 10
Pulse Secure example
F5 Edge Client example
SonicWALL Mobile Connect example
Login group or domain: This property can't be set in the VPN profile. Instead, Mobile Connect parses this value when the user name and domain are entered in the username@domain or DOMAINusername formats.
Example:
CheckPoint Mobile VPN example

Writing custom XML
For more information about writing custom XML commands, see each manufacturer's VPN documentation.
For more information about creating custom EAP XML, see EAP configuration.
Apps and Traffic Rules
Associate WIP or apps with this VPN: Enable this setting if you only want some apps to use the VPN connection. Your options:
- Associate a WIP with this connection: Enter a WIP domain for this connection
- Associate apps with this connection: You can Restrict VPN connection to these apps, and then add Associated Apps. The apps you enter automatically use the VPN connection. The type of app determines the app identifier. For a universal app, enter the package family name. For a desktop app, enter the file path of the app.
Important
We recommend that you secure all app lists created for per-app VPNs. If an unauthorized user changes this list, and you import it into the per-app VPN app list, then you potentially authorize VPN access to apps that shouldn't have access. One way you can secure app lists is using an access control list (ACL).
Network traffic rules for this VPN connection: Select the protocols, and the local & remote port and address ranges, are enabled for the VPN connection. If you don't create a network traffic rule, then all protocols, ports, and address ranges are enabled. After you create a rule, the VPN connection uses only the protocols, ports, and address ranges that you enter in that rule.
Conditional Access
Conditional Access for this VPN connection: Enables device compliance flow from the client. When enabled, the VPN client communicates with Azure Active Directory (AD) to get a certificate to use for authentication. The VPN should be set up to use certificate authentication, and the VPN server must trust the server returned by Azure AD.
Single sign-on (SSO) with alternate certificate: For device compliance, use a certificate different from the VPN authentication certificate for Kerberos authentication. Enter the certificate with the following settings:
- Name: Name for extended key usage (EKU)
- Object Identifier: Object identifier for EKU
- Issuer hash: Thumbprint for SSO certificate
DNS Settings

DNS suffix search list: In DNS suffixes, enter a DNS suffix, and Add. You can add many suffixes.
When using DNS suffixes, you can search for a network resource using its short name, instead of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN). When searching using the short name, the suffix is automatically determined by the DNS server. For example,
utah.contoso.comis in the DNS suffix list. You pingDEV-comp. In this scenario, it resolves toDEV-comp.utah.contoso.com.DNS suffixes are resolved in the order listed, and the order can be changed. For example,
colorado.contoso.comandutah.contoso.comare in the DNS suffix list, and both have a resource calledDEV-comp. Sincecolorado.contoso.comis first in the list, it resolves asDEV-comp.colorado.contoso.com.To change the order, select the dots to the left of the DNS suffix, and then drag the suffix to the top:
Name Resolution Policy table (NRPT) rules: Name Resolution Policy table (NRPT) rules define how DNS resolves names when connected to the VPN. After the VPN connection is established, you choose which DNS servers the VPN connection uses.
You can add rules to the table that include the domain, DNS server, proxy, and other details to resolve the domain you enter. The VPN connection uses these rules when users connect to the domains you enter.
Select Add to add a new rule. For each server, enter:
- Domain: Enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) or a DNS suffix to apply the rule. You can also enter a period (.) at the beginning for a DNS suffix. For example, enter
contoso.comor.allcontososubdomains.com. - DNS servers: Enter the IP address or DNS server that resolves the domain. For example, enter
10.0.0.3orvpn.contoso.com. - Proxy: Enter the web proxy server that resolves the domain. For example, enter
http://proxy.com. - Automatically connect: When Enabled, the device automatically connects to the VPN when a device connects to a domain you enter, such as
contoso.com. When Not configured (default), the device doesn't automatically connect to the VPN - Persistent: When set to Enabled, the rule stays in the Name Resolution Policy table (NRPT) until the rule is manually removed from the device, even after the VPN disconnects. When set to Not configured (default), NRPT rules in the VPN profile are removed from the device when the VPN disconnects.
- Domain: Enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) or a DNS suffix to apply the rule. You can also enter a period (.) at the beginning for a DNS suffix. For example, enter
Proxy
- Automatic configuration script: Use a file to configure the proxy server. Enter the proxy server URL that includes the configuration file. For example, enter
http://proxy.contoso.com/pac. - Address: Enter the IP address or fully qualified host name of the proxy server. For example, enter
10.0.0.3orvpn.contoso.com. - Port number: Enter the port number used by your proxy server. For example, enter
8080. - Bypass proxy for local addresses: This setting applies if your VPN server requires a proxy server for the connection. If you don't want to use a proxy server for local addresses, then choose Enable.

Split Tunneling
- Split tunneling: Enable or Disable to let devices decide which connection to use depending on the traffic. For example, a user in a hotel uses the VPN connection to access work files, but uses the hotel's standard network for regular web browsing.
- Split tunneling routes for this VPN connection: Add optional routes for third-party VPN providers. Enter a destination prefix, and a prefix size for each connection.
Trusted Network Detection
Trusted network DNS suffixes: When users are already connected to a trusted network, you can prevent devices from automatically connecting to other VPN connections.
In DNS suffixes, enter a DNS suffix that you want to trust, such as contoso.com, and select Add. You can add as many suffixes as you want.
If a user is connected to a DNS suffix in the list, then the user won't automatically connect to another VPN connection. The user continues to use the trusted list of DNS suffixes you enter. The trusted network is still used, even if any autotriggers are set.
Cisco Anyconnect Vpn Win 10
For example, if the user is already connected to a trusted DNS suffix, then the following autotriggers are ignored. Specifically, the DNS suffixes in the list cancel all other connection autotriggers, including:
- Always on
- App-based trigger
- DNS autotrigger
Anyconnect Vpn Cisco Download Windows 10
Next steps
The profile is created, but may not be doing anything yet. Be sure to assign the profile, and monitor its status.
Anyconnect Vpn Not Working Windows 10
Configure VPN settings on Android, iOS/iPadOS, and macOS devices.
